The gut microbiome is carefully regulated, and nutrition plays a significant role in this balance: consuming a nutritious diet boosts the overall cell count in the gut, whereas fasting diminishes it. The proportion of different cell types in the gut also changes depending on the nutritional status.
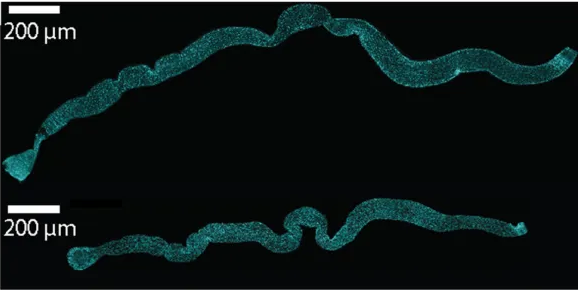 Microscope images of the fruit fly intestine where cell nuclei are stained (cyan). The intestine on the top is from well fed animal, and the intestine below from an animal kept on a restricted diet. Image Credit: Jaakko Mattila
Microscope images of the fruit fly intestine where cell nuclei are stained (cyan). The intestine on the top is from well fed animal, and the intestine below from an animal kept on a restricted diet. Image Credit: Jaakko Mattila
Comprehensive details on how the nutritional environment of the gut influences stem cell division and differentiation, and how stem cell responses to nutrients change with aging, are currently incomplete. "Nutrient adaptation" refers to the process by which nutrients guide cellular functions.
Scientists at the University of Helsinki have identified a new regulatory mechanism that governs the growth of intestinal stem cells according to dietary changes. Nutritionally induced cell signaling leads to larger stem cells in the intestines of fruit flies.
The size of these stem cells, in turn, influences the type of cell they will become. The ability to adjust stem cell size flexibly is essential for their functionality. In other words, cell size dynamically expands or contracts based on the dietary environment.
Stem cells' versatility allows them to transform to meet the prevailing dietary needs. The research revealed variations in how different sections of the intestine adapt the size of stem cells nutritionally and their subsequent specialization into different cell types.
Our observations demonstrate that the regulation of intestinal stem cells is much more region-specific than previously understood. This may be relevant to, for example, how we think about the pathogenetic mechanisms of intestinal diseases.”
Jaakko Mattila, Study Corresponding Author and Professor, Department of Biological and Environmental Sciences, University of Helsinki
Intermittent Fasting May Benefit Intestinal Stem Cells
Furthermore, the study revealed that older animals exhibit a markedly reduced ability of intestinal stem cells to adapt to changes in nutritional status. It was found that in older animals, stem cells tend to maintain a consistently large size, which hampers their ability to differentiate.
As the animals aged, those that had undergone intermittent fasting maintained a more robust capability to regulate stem cell size. Previous studies on intermittent fasting and its impact on the lifespan of animals indicate that the preservation of stem cell functionality could be a contributing factor to increased longevity.
The researchers suggest that the processes governing the activity, nutritional adaptation, and aging of stem cells in both humans and fruit flies share considerable similarities.
We believe that these findings have a broader significance towards understanding how to slow down the loss of tissue function caused by aging by controlling the nutrient adaptation of stem cells. However, more information is needed on the effect of the mechanism on human intestinal stem cells. Our work on the nutrient adaptation of stem cells continues.”
Ville Hietakangas, Professor, Department of Biological and Environmental Sciences and the Institute of Biotechnology, University of Helsinki
Source:
Journal reference:
Mattila, J., et.al., (2024). Stem cell mTOR signaling directs region-specific cell fate decisions during intestinal nutrient adaptation. Science Advances. doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adi2671