Mendelian randomization, a key method in medical research, aids in determining whether certain factors actually cause disease.
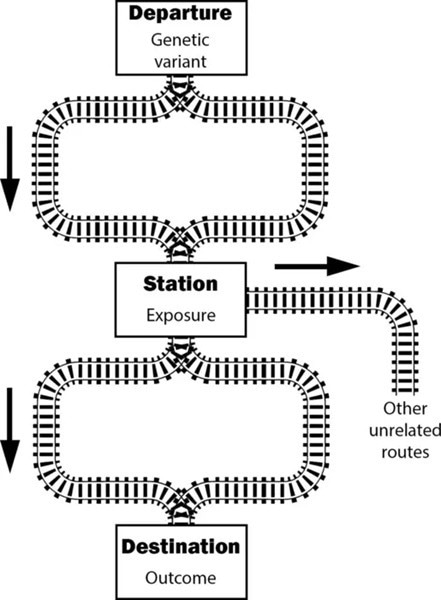 The instrument variable assumptions imply that all trains leaving the departure station (genetic variant) and arriving at the destination (outcome) must pass through the exposure station. They can take different routes, reflecting different causal pathways, and there can be some pathways from the exposure to unrelated destinations. But the exposure station must be a station stop on all routes from the variant to the outcome. Image Credit: By Stephen Burgess and Héléne Toinét Cronjé
The instrument variable assumptions imply that all trains leaving the departure station (genetic variant) and arriving at the destination (outcome) must pass through the exposure station. They can take different routes, reflecting different causal pathways, and there can be some pathways from the exposure to unrelated destinations. But the exposure station must be a station stop on all routes from the variant to the outcome. Image Credit: By Stephen Burgess and Héléne Toinét Cronjé
This methodology employs genetic variations as “natural experiments” to unveil cause-and-effect associations. Nonetheless, selecting appropriate genetic variations is imperative to ensure precise outcomes.
Consider a train system in which the initial point is the genetic variation, a station represents the exposure, and the final destination is the disease. The train must pass through the exposure station on its way to the disease. This concept illustrates the fundamental principle of Mendelian randomization: genetic variation impacts the exposure, subsequently affecting the disease's occurrence.
Biologically driven methods are favored when choosing genetic variations. These methods concentrate on genes that are closely associated with the exposure, such as utilizing variations within a gene that encodes a protein to comprehend the protein’s effect on the disease. This method is considered more dependable as it reduces extraneous influences on the disease.
Conducting genome-wide analyses, despite their extensive data, may result in misleading outcomes. The abundance of information can introduce inaccuracies and diminish the clarity of the findings, ultimately resulting in unreliable conclusions. Like trains traveling in various directions, these analyses lack the targeted approach of biologically driven methods.
However, genome-wide analyses can still provide valuable assistance as corroborating proof. Envision a scenario where numerous trains depart from various stations, yet all ultimately converge at the exposure station. If these trains consistently arrive at the disease destination, it bolsters the evidence supporting a causal connection.
The main lesson to be learned? Give priority to biologically driven methods whenever feasible. Although not always achievable, they provide more accurate understandings. Genome-wide analyses should be used with caution to provide supplementary evidence, but their constraints must be considered.
The collaboration between experts in biology and statistics is crucial to draw causal conclusions from Mendelian randomization accurately. This interdisciplinary partnership guarantees that we remain focused on comprehending the genuine factors behind diseases.
Source:
Journal reference:
Burgess., et al., (2024) Incorporating biological and clinical insights into variant choice for Mendelian randomization: examples and principles. eGastroenterology. doi.org/10.1136/egastro-2023-100042