In 2012, the Harvard Business Review dubbed data scientists the sexiest job of the 21st century. Given the rapidly increasing number of sources from which data is now available, thanks to the maturing field of the Internet of Things, it is unsurprising that the growing field of data science has accelerated in popularity.

Image Credit: metamorworks/Shutterstock.com
Data sciences encompass numerous disciplines, including math, statistics, artificial intelligence (AI), advanced analytics, specialized programming, and machine learning. Its goal is to pull out actionable insights from a wealth of data that might derive from multiple sources. These insights can be used to guide decision-making.
Data science is important to many applications, such as gaming, targeted advertising, speech, and image recognition technology, fraud and risk detection, and many more. Perhaps its most important role is its use in life sciences.
Applications of data science in the life sciences
The adoption of data science is revolutionizing the life sciences sector. The applications of data science in the life sciences are vast and growing. Pharmaceuticals, surgery, disease management, and more are all being advanced by data science. Here, we discuss the key ways in which data science is impacting the life sciences right now.
Drug discovery
While medical science has made great advances over the last century, we have eradicated several illnesses and have made significant improvements in the prevention, treatment, and management of others, but we still need new drugs. The medical sector faces the challenge of developing new treatments for patients who do not respond to conventional treatments, as well as the serious problem of increasing antibiotic resistance. Therefore, much time and effort is put into drug discovery and development, where around $200 billion is invested annually.
For several years, AI has been leveraged to improve drug discovery, using algorithms to automatically screen thousands of potential therapeutic compounds to identify those with the desired features or activity. In this way, data science speeds up and reduces the failure rate of drug development.
Virtual assistance
Data science is also being leveraged into virtual assistance applications, where chatbots and AI platforms provide people with accurate and relevant information about their health, guiding them to take the right actions for their situation.
Wearables
Wearables are an increasingly important fragment of the healthcare sector. Here, data science is leveraged to make intelligent insights about a person’s health state by analyzing sources such as heart rate, sleep patterns, and more, which can be used to encourage healthy activities.
Studies have shown that next-generation wearables could theoretically detect some diseases before patients are likely to recognize symptoms and seek medical attention.

Image Credit: KANUT PHOTO/Shutterstock.com
Health management
Wearables are also being used as tools to track patient health. Parameters such as heart rate, brain activity, blood glucose, sleep patterns, and stress levels can all be monitored via wearable devices. Once analyzed with machine learning algorithms, doctors can access useful insights that indicate the patient’s health status. This allows doctors to monitor how a patient is recovering or identify if they have common conditions such as cardiac or respiratory diseases.
Diagnostics
Data science is also being used to improve diagnostics. The digitization of health records has opened the door to the early detection of diseases and health issues. In addition, data science can use this information to generate heatmaps that show demographic patterns of ailments that can be used to produce potentially actionable insights.
Predictive analytics
Data science is being leveraged into an emerging field of life sciences called predictive analytics. Models of predictive analytics leverage historical data to identify patterns and produce accurate predictions pertaining to healthcare.
Predictive analytics can take data from multiple sources and correlate and associate these data points to particular symptoms, actions, and even diseases. This helps doctors gain a clearer picture of a person’s health. For example, analytics can assist in revealing the stage of a disease, the damage that has occurred, and the most appropriate treatment route.
Predictive analytics are already being used to manage chronic diseases, predict future patient crises, deliver faster hospital data documentation, and monitor and analyze the demand for pharmaceutical logistics.
Medical imaging
Finally, data science is making big waves in medical image analysis. CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays are all commonplace in hospitals. However, highly skilled technicians must ascertain any important information from the images generated via these techniques. Additionally, there are limits to what the human eye can pick up on. Now, data science is being used to detect minute aspects of these images with the help of machine learning algorithms.
Studies have shown that this technology can help identify clinically relevant information more successfully than human technicians. For example, recently, a head-to-head demonstrated that AI was superior to humans at analyzing heart scans. More work is underway to develop and improve these techniques.
We might see AI as the standard for reading medical scans in the future.
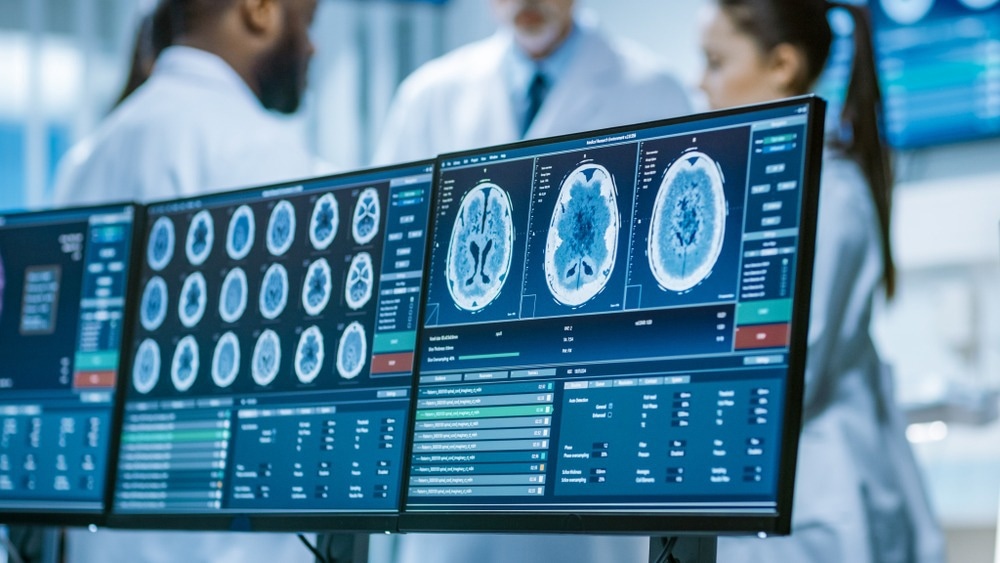
Image Credit: Gorodenkoff/Shutterstock.com

 Read Next: Applications of Big Data in Life Sciences
Read Next: Applications of Big Data in Life Sciences
Sources:
- Data Science [online]. IBM. Available at: https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/data-science-introduction (Last accessed December 2022)
- Kristen Houser. 2022. First-of-its-kind trial shows AI beat humans at analyzing heart scans [online]. Free Think. Available at: https://www.freethink.com/health/lvef-echonet (Last accessed December 2022)
- Life Science Data: Why Big Data, AI & Analytics Matter [online]. Weka. Available at: https://www.weka.io/learn/hpc/life-science-data (Last accessed December 2022)
- Subrahmanya, S.V. et al. (2021) “The role of Data Science in healthcare advancements: Applications, benefits, and future prospects,” Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -), 191(4), pp. 1473–1483. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-021-02730-z.