This article is based on a poster originally authored by Michael Jones1 Chris Henry1 , Ashley Sage1 , Scott Campbell2 and was presented at ELRIG Drug Discovery 2023.
1Waters Corporation 2SpectralWorks LTD

Many organic chemists employ mass spectrometry (MS) as a convenient verification tool for their product, and for any impurities present in a synthetic reaction.
Single quadrupole mass spectrometers provide only nominal mass data, which, while useful, does not eliminate the potential of misassignment of the target compound, degradants, impurities, or side reaction products. Increased confidence through compound characterization is possible through the accurate mass measurements provided by Time of Flight (ToF) high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS), which can require high levels of expertise to operate.
Within this body of work, we will demonstrate a routine high-resolution mass spectrometer combined with a browser-based ‘walk up’ software for simple access to accurate mass measurements for synthetic chemists.
Methods
Sample Preparation
To demonstrate this workflow a standard of ramipril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor was spiked at 0.1 % (w/w) with four related impurities; ramipril isopropyl ester, ramipril diketopiperazine, ramipril methyl ester and hexahydroramipril labelled A-D respectively, and analyzed using the ACQUITY™ RDa™ detector.
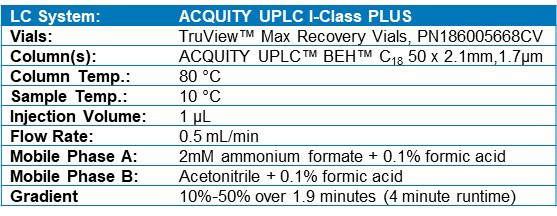
Method details and instrument parameters are detailed in Table 1.
The chemical structures of ramipril and its potential related impurities are shown in Figure 1.
Sample submission and processing was controlled by RemoteAnalyzer® software (SpectralWorks Ltd.), while data acquisition was carried out by UNIFI™ software within the waters_connect™ platform. The acquired raw data remains intact and independent of the RemoteAnalyzer processing.
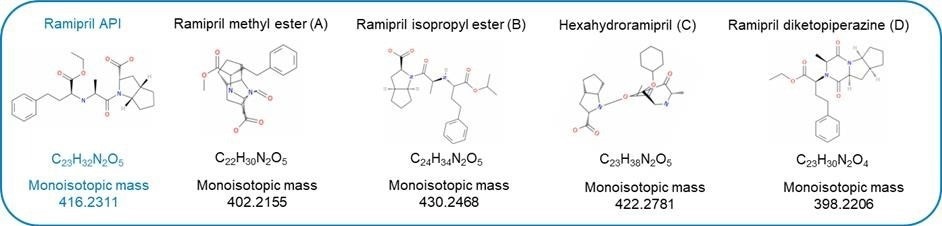
Figure 1. Ramipril API and four related impurities.

Table 1. LC-MS conditions.
On submission of the sample, an email was sent to the submitter to confirm the analysis request was successfully received. On completion of the sample analysis, an email was received confirming the successful status.

Figure 2. Steps 1-6 detailing the workflow steps involved when submitting and processing samples on RemoteAnalyzer.
Results
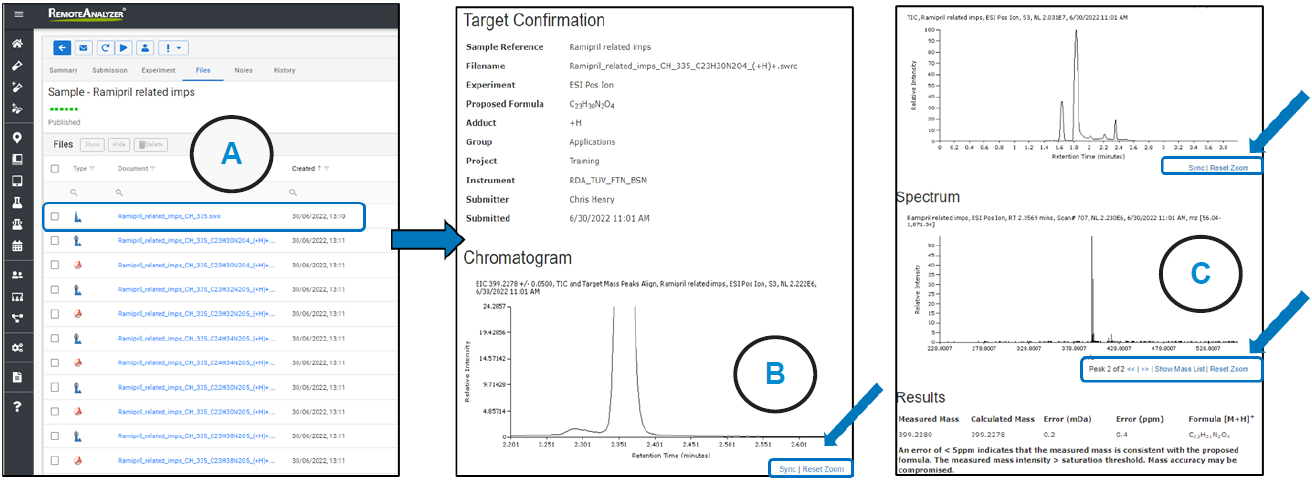
Figure 3. Results page with interactive chromatograms/spectra.
The emailed result contained a .pdf document for every proposed formula. In addition, a hyperlink was present in the email, which, when clicked, took the analyst to a sample review page within the RemoteAnalyzer software Figure 3A.
This contained copies of the .pdf’s along with links to .swrc. files (RemoteAnalyzer propriety file format) for each component detected. When .swrc files are selected, an interactive results page opens with ‘zoom enabled’ TIC Figure 3B, along with EIC’s and extracted spectrum for each analyte Figure 3C.
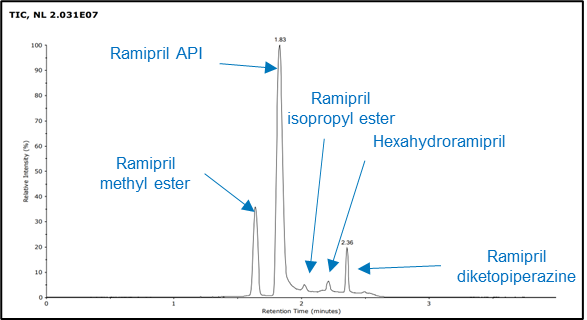
Figure 4. TIC from RemoteAnalyzer software.
Table 2. Summarised results for ramipril and related impurities.
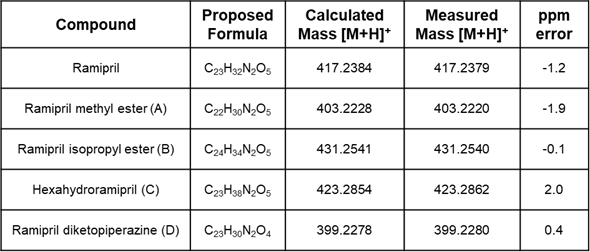
Figure 4. shows the TIC from the RemoteAnalyzer software report demonstrating the successful separation of all five components within the four-minute runtime. The results for the measured mass and ppm error for the five compounds have been summarized in Table 2. All mass errors were calculated as less than or equal to 2 ppm.
Discussion
The ACQUITY RDa Detector was set up automatically, including detector, auto-tune and mass calibration. Following this set up, MS full scan accurate mass data were acquired at a capillary voltage of 1.5 kV and a cone voltage of 30 V.
The samples were submitted to RemoteAnalyzer using a web browser. Samples were scanned and placed into position using the barcode scanner situated at the instrument, and the results were automatically emailed in .pdf format.
The chromatography showed slight co-elution of the isopropyl ester impurity and the API; however, the increased specificity of full scan time of flight detection allows for the accurate quantitative integration and assignment of closely eluting peaks2.
All compounds of interest exhibited excellent mass accuracy of ≤ 2 ppm.
Sample submission and processing were controlled by the RemoteAnalyzer software, while data acquisition was carried out by the UNIFI application, with the acquired raw data remaining intact and independent of the RemoteAnalyzer processing.
Conclusion
- Combining the ACQUITY RDa Detector with the RemoteAnalyzer software provides routine access to accurate mass measurements for synthetic chemists.
- Ramipril and the four spiked-related substances were all detected with excellent mass accuracies of ≤2 ppm using a four-minute UPLC run time.
- With more data points collected across a peak compared to single quadrupole detection, the RDa detector enables the use of rapid UPLC gradients without compromising qualitative mass measurements.
- The straightforward operation with easy-to-use hardware and web-based software provided scientists access to accurate mass measurements, enabling them to make critical decisions with confidence under time constraints.
References
- A Review of Waters Hybrid Particle Technology. Part 2: Ethylene Bridged [BEH Technology™] Hybrids and Their Use in Liquid Chromatography. 720001159EN
- Alelyunas YW, Wrona MD, Cook K, McDonald S, Rainville P: Effect of MS Scan Speed on UPLC Peak Separation and Metabolite Identification: Time-of-Flight HRMS v Orbitrap. March 2013 720004762EN
Please note: ‘ACQUITY’, ‘RDa’, ‘UPLC’, ‘BEH’, ‘UNIFI’ and ‘TruView’ are all registered trademarks of Waters Corporation. ‘RemoteAnalyzer’ is a registered trademark of SpectralWorks Ltd.
Last Updated: Jul 8, 2024