pH is a measurable parameter between the values of 0 and 14, provided the concentration of the solution does not exceed 1M. Solutions with a pH<7 are acidic, whereas those with a pH>7 are alkaline. A pH meter is a device that measures the changes in the activity of hydrogen ions in a solution.
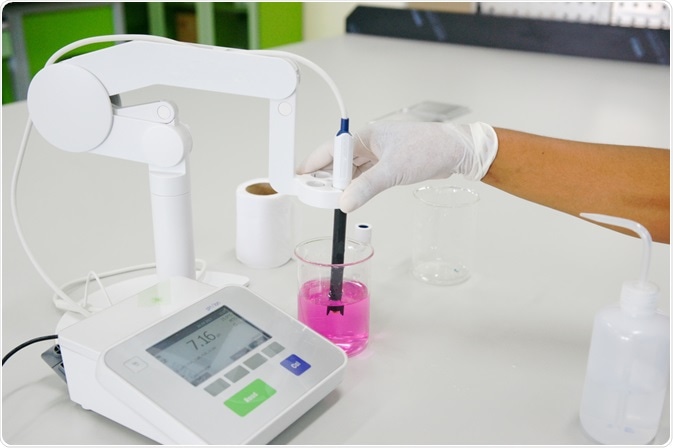 Image Creedit: Choksawatdikorn /Shutterstock.com
Image Creedit: Choksawatdikorn /Shutterstock.com
What are acids and alkalis?
According to the Arrhenius definition, acid is any substance that produces dissociated hydrogen (H+) ions or hydronium ions H3O+ when it is dissolved in water. A base is a substance that produces dissociated hydroxyl (OH-) ions when it is dissolved in water.
The concept of pH was proposed by the Danish chemist Søren Peder Lauritz Sørensen in 1909. The pH quantifies the H+ ions in a solution. The notional definition of pH is logarithmic of the reciprocal of hydrogen ion activity, aH+, in a solution:
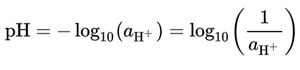
Equation 1. The notational definition of pH expressed in mathematical terms.
The pH is directly related to the proton concentration only when the solution is very dilute. However, pH is accurately determined by pH-sensitive, ion-selective electrodes which respond to proton activity, rather than changes in proton concentration. The notional definition of pH is therefore discarded and ideally defined according to the Nernst equation, which for the H+ ion can be expressed as follows:
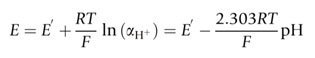
Equation 2. The operational expression of pH. The electrode potential (E) of a pH-sensitive electrode follows the Nernst equation as shown. The definition of the parameters is included in the text.
E is the measured potential, E’ is a standard electrode potential (i.e., the constant value of the electrode potential for aH+ = 1, and the specific electrode/solution conditions for each case), R is the gas constant, T is the temperature in Kelvin, F is the Faraday constant. The pH-sensitive, ion-selective electrode is a linear function of the pH when the pH is defined as a measure of proton activity.
pH meters
pH meters are electronic devices comprised of a special measuring probe (a glass electrode or, an ion-selective field-effect transistor (ISFET), in specialized cases), attached to an electronic meter that displays the decimal pH reading. The pH meter must be calibrated prior to use against buffer solutions of known hydrogen ion activity.
Using a pH Meter
The standard methodology for measuring pH
pH meters consist of a glass electrode made of a specialty glass membrane that is sealed at the end forming a bulb. Inside the glass is an internal standard acidity solution, usually 0.1 M HCl, along with an internal reference electrode, REin (typically an Ag/AgCl wire electrode). This solution is called the reference solution of known pH, 7.
A second electrode REext is placed in an external tube immersed in KCl. This external tube forms a concentric enclosure around the first enclosed glass tube containing the 0.1 M HCl (the internal tube).
The external tube is made of pH-sensitive glass and is in contact with the test solution through an opening called a porous diaphragm. The inclusion of a reference electrode encased by the internal tube is necessary as its pH is known and can be compared to a test solution so that its pH value can be determined. This set-up is called a combination pH electrode.
Operation of pH meter
The pH meter operates like a voltmeter. The pair of electrodes in the combinatorial set-up can measure small changes in voltage (also called potential difference) in the order of millivolts. Changes in potentials are caused by the loss of electrons that correspond with the loss of H+.
The voltage produced by the test solution is measured and compared with the voltage produced by the reference solution which is exposed to the test solution via the porous diaphragm. The difference in the voltage between the two is used to calculate the pH:
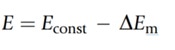
Econst refers to the potential difference of the reference electrode and DEm is the change in the potential difference of the external glass membrane caused by the external test solution and internal KCl solution. DEm can be calculated using the Nernst Equation:
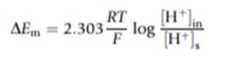
Calibration
The pH meter should be calibrated before each measurement using at least two standard buffer solutions of known pH values (typically around 4 and 7).
Further Reading
Last Updated: Sep 22, 2022