When cells develop, variations in the interaction of genes of an individual determine their fate. Such variations in genetic interactions can make the individual’s cells powerful against infection from viruses or enable the immune cells to kill the tumor cells.
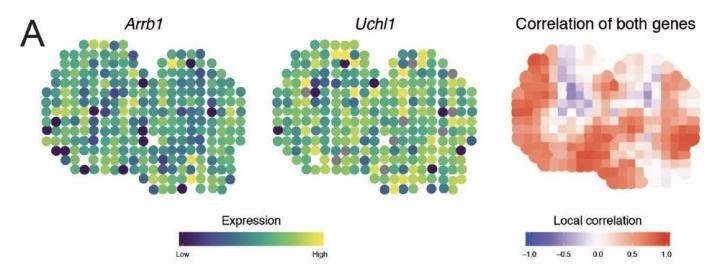
Mapping correlation between genes within a mouse olfactory bulb. Image Credit: Springer Nature/University of Sydney.
Gaining insights into how these gene associations work over the development of human tissue and organs is crucial to formulate medical treatments for complicated disorders like developmental disorders, cancer, or heart disease.
A novel technology known as single-cell RNA-sequencing has made it feasible to investigate the behavior of genes in mammal and human cells at an unparalleled resolution and has the potential to speed up medical and scientific discoveries.
Researchers from the University of Sydney collaborated with scientists from China, the United States, and the United Kingdom to develop an analytical method for this single-cell sequencing, which can investigate for wider changes in the behavior of genes within human tissue. It has been referred to as single-cell higher-order testing (scHOT).
The researchers have demonstrated the efficacy of this approach in a paper recently published in the Nature Methods journal, by finding genes in mice whose variability varies in cells during embryonic liver development.
Moreover, the research group headed by Professor Jean Yang in the School of Mathematics and Statistics has identified new pairs of genes that co-vary in expression across the mouse olfactory bulb, a tissue crucial for understanding neurodevelopmental diseases.
These study results collectively show that scHOT is a robust, novel tool that will unravel hidden gene associations in the cells of an individual and enable the complete exploration of these advanced single-cell technologies to make significant biological discoveries.
This study will help find out the hidden gene associations in the cells of an individual, thus offering a new technique to visualize and explain biological complexity.
This study forms part of a series of single-cell data science tools created by the bioinformatics research team at the University of Sydney.
Source:
Journal reference:
Ghazanfar, S., et al. (2020) Investigating higher-order interactions in single-cell data with scHOT. Nature Methods. doi.org/10.1038/s41592-020-0885-x.