Medical cannabis is a highly debated topic, but there is still a lot more to learn about this compound. A research team from the Department of Neuroscience at the Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences has now made a recent finding that may prove crucial to upcoming studies and treatments using medical cannabis.
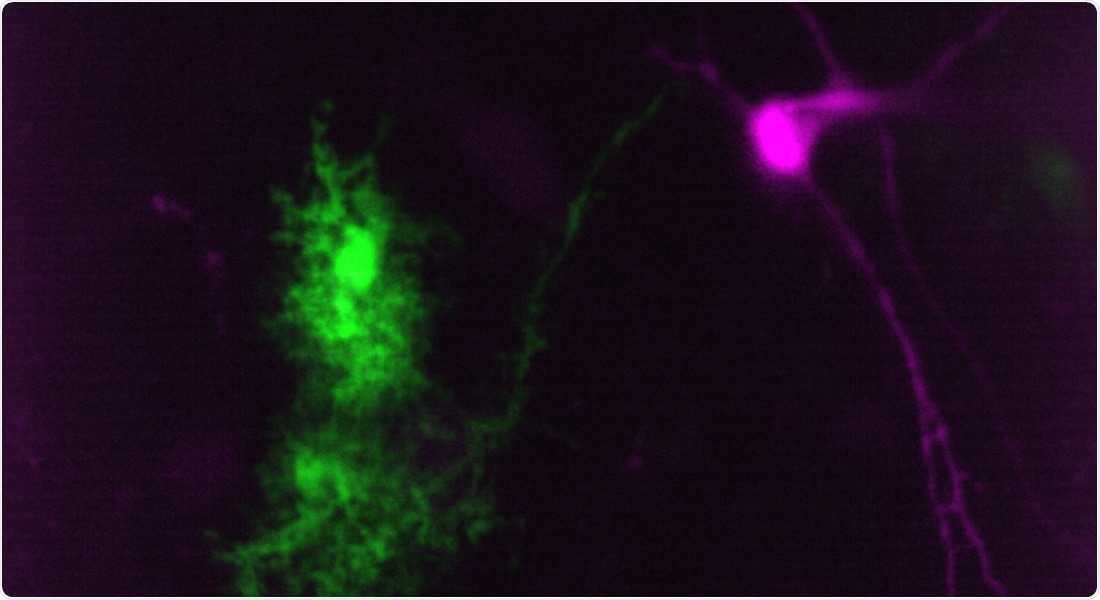
Neurons from the spinal cord (pink) are in constant dialogue with astrocytes (green). They use cannabinoids as a signaling molecule. Image Credit: Alexia Montalant.
Cannabinoids are compounds present in cannabis and they can also be found in the central nervous system. The researchers used a mouse model to prove that a particular synthetic cannabinoid, called cannabinoid WIN55,212-2, decreases essential tremors by stimulating the support cells of the brain and spinal cord, called astrocytes. Prior studies into medicinal cannabis have targeted the nerve cells or the supposed neurons.
We have focused on the disease essential tremor. It causes involuntary shaking, which can be extremely inhibitory and seriously reduce the patient’s quality of life. However, the cannabinoid might also have a beneficial effect on sclerosis and spinal cord injuries, for example, which also cause involuntary shaking.
Jean-François Perrier, Research Head and Associate Professor, Department of Neuroscience, University of Copenhagen
“We discovered that an injection with the cannabinoid WIN55,212-2 into the spinal cord turns on the astrocytes in the spinal cord and prompts them to release the substance adenosine, which subsequently reduces nerve activity and thus the undesired shaking,” Perrier added.
Targeted treatment with no problematic side effects
The fact that astrocytes are partly responsible for the impact of cannabis provides a whole new method for understanding the medical effects of this compound and can help enhance the treatment of patients afflicted with involuntary shaking.
The spinal cord accounts for the majority of human movements. When the motor neurons in the spinal cord are stimulated, both spontaneous and voluntary movements are also activated. The motor neurons link the spinal cord with the muscles, and whenever a motor neuron transmits impulses to the muscles, it causes contractions and thus movements.
But when the motor neurons send out contradictory signals simultaneously, involuntary shaking takes place. And that is why the research team has focused its efforts on the spinal cord.
One might imagine a new approach to medical cannabis for shaking, where you – during the development of cannabis-based medicinal products – target the treatment either at the spinal cord or the astrocytes – or, at best, the astrocytes of the spinal cord.”
Eva Carlsen, Postdoc, University of Copenhagen
Most of the tests were done by Carlsen during her Ph.D. and postdoc studies.
“Using this approach will avoid affecting the neurons in the brain responsible for our memory and cognitive abilities, and we would be able to offer patients suffering from involuntary shaking effective treatment without exposing them to any of the most problematic side effects of medical cannabis,” Carlsen concluded.
The subsequent step is to perform clinical trials on people suffering from essential tremors to find out if the new method has the same impact on human beings.
Source:
Journal reference:
Carlsen, E. M. M., et al. (2021) Spinal astroglial cannabinoid receptors control pathological tremor. Nature Neuroscience. doi.org/10.1038/s41593-021-00818-4.