Pichia pastoris (syn. Komagataella phaffii) is a model methylotrophic yeast that can easily realize high-density fermentation. Thus, it is regarded as a potential chassis cell for efficient biotransformation of methanol.
Establishing an efficient genetic engineering platform for metabolic engineering of Methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Image Credit: Peng Cai.
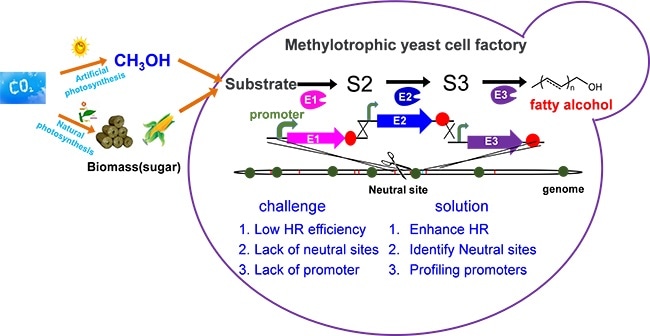
But its metabolic engineering toward industrial use is hampered by the lack of synthetic biology tools and inefficient gene editing.
A team of researchers headed by Prof. Yongjin Zhou from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently determined an efficient genetic engineering platform in Pichia pastoris.
The research was published on July 1st, 2021, in Nucleic Acids Research.
The team created innovative genetic tools to achieve accurate precise genome editing in Pichia pastoris by improving homologous recombination (HR) rates and engineering the multiple intrusion-induced rearrangement (MIR) processes. RAD52, the key gene that has a vital role in HR repair in Pichia pastoris, was overexpressed to enhance the efficiency of single gene editing to 90%.
Moreover, the researchers increased multi-fragment recombination efficiency at a single site by 13.5 times, thus identifying and characterizing 18 promoters and 46 neutral sites for gene expression and genome integration.
Lastly, the team created a two-factorial regulation system for controlling fatty alcohol biosynthesis in Pichia pastoris from a different carbon source.
This advanced gene editing systems can theoretically realize stable loading of more than 100 exogenous genes and precise regulation of gene expression in Pichia pastoris, which will provide convenience for the synthetic biology research of Pichia pastoris. It also provides insights for metabolic engineering of other unconventional yeast.”
Yongjin Zhou, Professor, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Dalian Science and Technology Innovation Funding.
Source:
Journal reference:
Cai, P., et al. (2021) Recombination machinery engineering facilitates metabolic engineering of the industrial yeast Pichia pastoris. Nucleic Acids Research. doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab535.