Deep learning model developed by researchers outperform human fishermen in correctly identifying the gender of horsehair crabs.
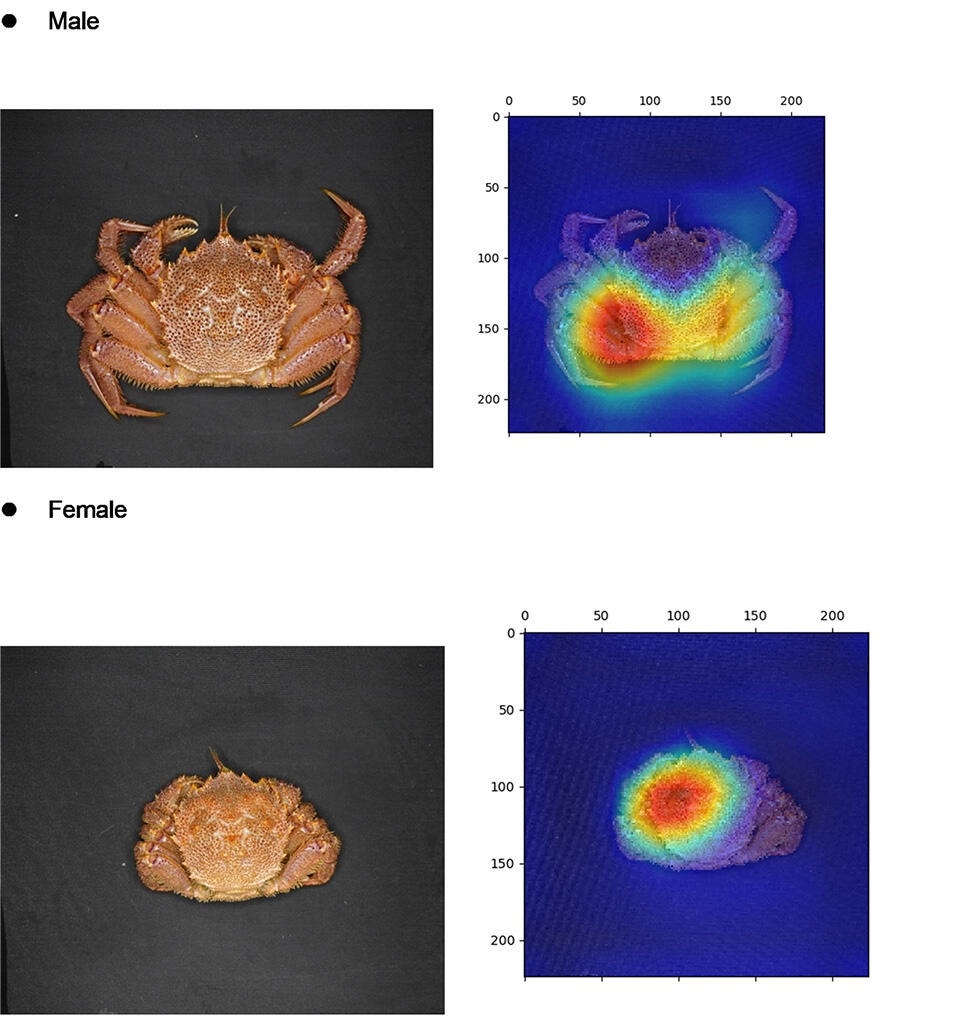
Deep learning models help tell apart male and female horsehair crabs. The heatmaps highlight the specific parts of the shell that the proposed artificial intelligence algorithms “focus on” when classifying male and female crabs. These models can vastly outperform humans in this task and may find applications in crab aquaculture and responsible fishing. Image Credit: Shin-ichi Satake from Tokyo University of Science, Japan.
When winter comes to Japan, fishermen in the northern regions set out to capture one of the most anticipated seasonal delicacies: the horsehair crab. Known locally as “kegani” and bearing the scientific name Erimacrus isenbeckii, this species of crustacean is highly sought after throughout the country. To protect the horsehair crab population from overfishing, the Japanese and prefectural governments have implemented various restrictions on their capture. For example, in Hokkaido, where kegani is abundant, capturing females for consumption is strictly prohibited.
To comply with these laws, experienced fishermen have learned how to tell apart males from females through visual inspection. While it is relatively straightforward to distinguish them by looking at the underside (abdomen) of the crabs, doing so by looking at their shell side is much more challenging. Unfortunately, when captured crabs settle on board a ship, they almost always do so with their shell side pointing up, and picking them up and flipping them individually to determine their sex is time-consuming.
Could this be yet another task artificial intelligence (AI) may excel at? In a recent study, a research team from Japan, including Professor Shin-ichi Satake from Tokyo University of Science (TUS), Japan, sought to answer this question using deep learning. Their latest paper, published in the renowned journal Scientific Reports, is co-authored by Associate Professor Yoshitaka Ueki and Professor Ken Takeuchi from TUS and Assistant Professor Kenji Toyota and Professor Tsuyoshi Ohira from Kanagawa University.
The researchers implemented three deep convolutional neural networks based on three well-established image classification algorithms: AlexNet, VGG-16, and ResNet-50. To train and test these models, they used 120 images of horsehair crabs captured in Hokkaido; half of them were males, and the other half were females. A notable advantage of these models is that they are “explainable AI.” Simply put, it means given an image of a crab, it is possible to see what specific regions of the image were relevant for the algorithm to make its classification decision. This can reveal subtle differences between the males and females that could be useful for manual classification.
The test results were quite promising in terms of accuracy and performance metrics, as Prof. Satake highlights: “Even though gender classification was virtually impossible by human visual inspection on the shell side, the proposed deep learning models enabled male and female classification with high precision, achieving an F-1 measure of approximately 95% and similarly high accuracy values.” This means that the AI approach vastly outperformed humans and provided consistent, reliable classification.
Interestingly, when observing the heatmaps, which represented the regions the models focused on for classification, the team found significant differences between the sexes. For one, the heatmap was enhanced near the genitalia shape on the abdomen side. When classifying males, the algorithms focused on the lower part of the carapace. In contrast, when classifying females, the algorithms focused on the upper portion of the carapace. This could provide useful information not only for the development of future AI sex classification models for crabs but also shed light on how experienced fishermen can tell apart males from females apart even when looking at their shell side.
Considering that being captured can be a great source of stress for crabs, being able to quickly tell females apart without flipping them before release could help prevent health or reproductive problems for these crabs. Thus, deep learning could potentially be an important tool for enhancing conservation and farming efforts. “The fact that deep learning can discriminate male and female crabs is an important finding not only for the conservation of these important marine resources but also for the development of efficient aquaculture techniques,” remarks Prof. Satake.
Notably, implementing AI classification techniques directly on ships could reduce the amount of manual work and make crab fishing more cost-effective. Moreover, the proposed models could be retrained and repurposed for the gender classification of other species of crabs, such as the blue crab or the Dungeness crab.
Overall, this study showcases how AI can be leveraged in creative ways to not only make people’s work more efficient but also have a direct positive effect on conservation, responsible fishing, and sustainability of crab aquaculture.