The most common extracranial solid tumor, called neuroblastoma, is often diagnosed during childhood. It is responsible for causing 15% of all malignancy death in childhood.
Functional exploration of neuroblastoma associated DDX1 gene polymorphism rs72780850. Image Credit: ©Science China Press.
While advanced immunotherapies and numerous cytotoxic treatments have been used, the survival rate of this tumor continues to be below 50%.
The genetic basis of sporadic neuroblastoma also continues to be vague. While achievements have been remarkable, the detected risk variants were just a small part of the variants associated with neuroblastoma.
DNA chip-based GWAS tends to miss a few functional polymorphisms. Hence, the supplementary predisposing variants of neuroblastoma, particularly based on numerous populations, still need to be identified.
According to the screening strategy of functional gene polymorphism, we have achieved some results. For example, screening strategy designed for polymorphism targeted by MYCN and important functional gene polymorphism sites missed by GWAS chip.”
Yongli Guo, Study Corresponding Author and Professor, Science China Press
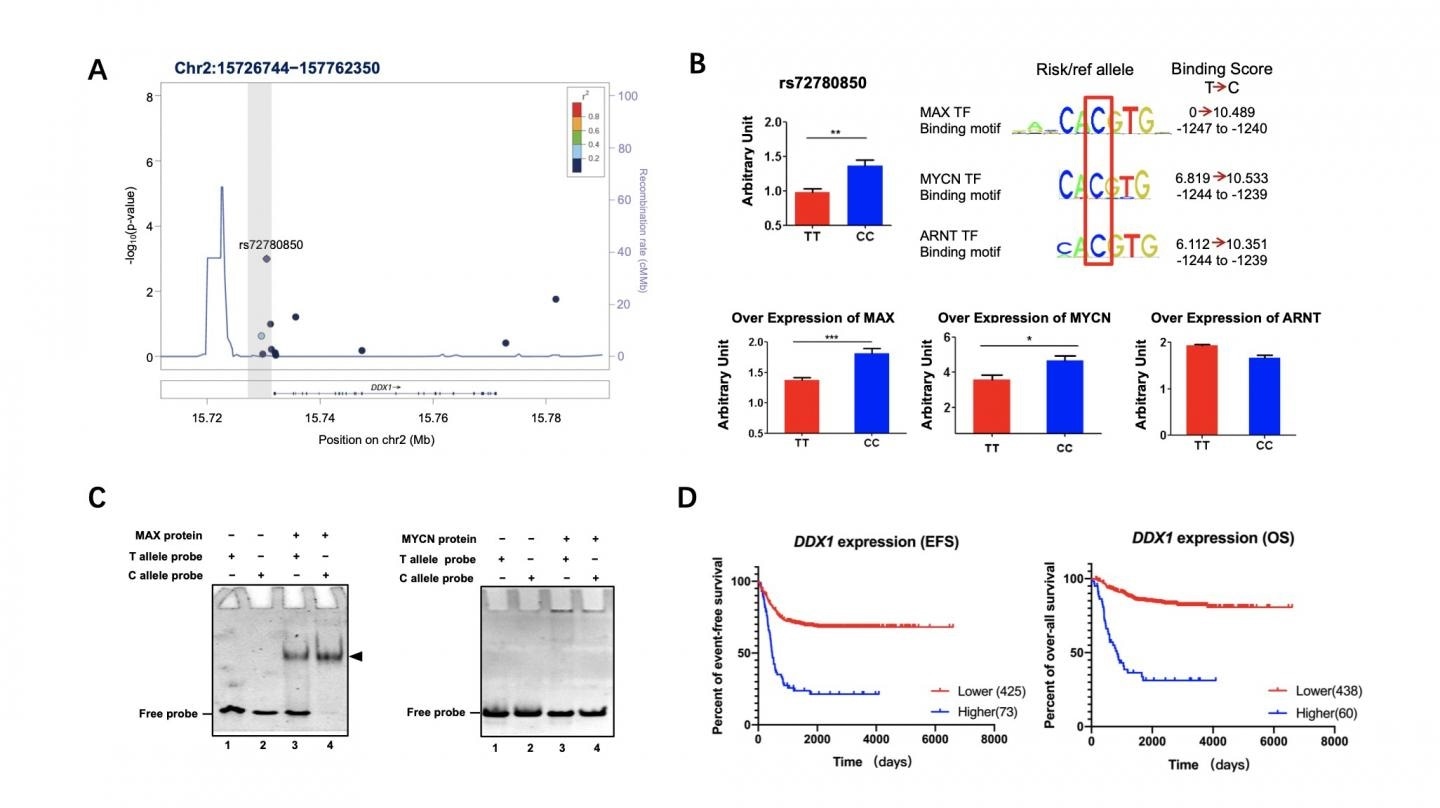
Guo continued, “Colleagues are concerned about why are we focused on the DDX1 gene this time. Interestingly, DDX1 loci locates very close to MYCN gene, it was predicted that it may be cis-regulated by MYCN. And we have found that highly expressed DDX1 is close associated to poor survival of neuroblastoma.”
The study’s authors showed that genetic variation, resulting in increased expression of the DDX1 gene, is linked to susceptibility to neuroblastoma.
MAX is the binding partner of the oncogenic transcription factor MYCN. Its binding affinity to DDX1 promoter rs72780850 C allele is higher than T allele. Interestingly, MYCN can active the reporter activity of DDX1 promoter, but cannot bind to the promoter alone. This result consistants with the way of MYCN working, like all members of the MYC family, requiring interaction with members of the MAX family to form a functional transcription factor.”
Dr Yaqiong Jin, Study First Author, Science China Press
The researchers’ study methodically unravels the association between MYCN-associated variants and susceptibility to neuroblastoma in the Chinese population, and offers the mechanisms about the working of this variant.
Source:
Journal reference:
Jin, Y., et al. (2020) MYC-associated protein X binding with the variant rs72780850 in RNA helicase DEAD box 1 for susceptibility to neuroblastoma. SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences. doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1784-7.