Due to its accumulation in crops, specifically rice, cadmium (Cd), a hazardous heavy metal contaminant of cultivated land, poses a threat to human health. Thus, it is vital to develop methods to prevent Cd from accumulating in rice grains.
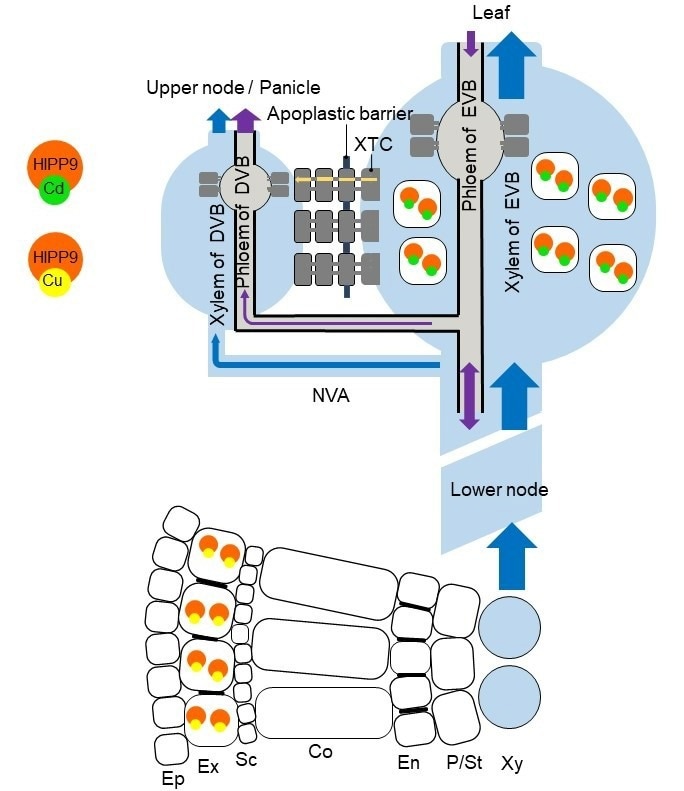 Schematic diagram showing the roles of OsHIPP9 in the retention of Cd and Cu in rice. Image Credit: IBCAS
Schematic diagram showing the roles of OsHIPP9 in the retention of Cd and Cu in rice. Image Credit: IBCAS
In rice, Cd is transferred from the soil to tissues above ground via the roots. To guide Cd in rice, the nodes, which are vascular bundles connecting to the roots, leaves, and panicles, are crucial.
Through the use of a Cd tolerance yeast screening system, a research team led by Prof. Leqing Qu from the Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IBCAS) discovered the Cd metallochaperone OsHIPP9 (heavy metal-associated isoprenylated plant protein 9) and characterized its role in rice using genetic, cellular, and biochemical methods.
OsHIPP9 has Cd and Cu binding capacity, which is mostly dependent on the thiol in cysteines to create a stable metal-protein complex. In rice, OsHIPP9 is mostly expressed in the xylem region of expanded vascular bundles at nodes and the root exodermis.
OsHIPP9 knockout increased Cd concentrations in upper nodes and panicles but lowered Cd in expanded leaves, probably owing to alterations in Cd distribution in the nodes.
Moreover, OsHIPP9 overexpression raised the Cu concentration in rice plants, whereas OsHIPP9 knockout lowered the Cu concentration in aboveground tissues in rice.
These findings provided important information for controlling Cd and Cu levels in rice grains by revealing the dual metallochaperone roles of OsHIPP9, which chelate Cd in the xylem region of EVB for Cd retention in the nodes and chelate Cu in rice roots to assist Cu uptake.
OsHIPP9 may mediate more Cd migration into the leaves rather than into the grain, which is crucial for reducing Cd levels in the grain.”
Dr. Shuo Xiong, Study First Author, Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Source:
Journal reference:
Xiong, S., et al. (2023). Metallochaperone OsHIPP9 is involved in the retention of cadmium and copper in rice. Plant, Cell & Environment. doi.org/10.1111/pce.14576