Reviewed by Danielle Ellis, B.Sc.Dec 15 2023
In a recent research, scientists from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai unveiled LoGoFunc, an innovative computational tool designed to forecast both pathogenic gain- and loss-of-function variants throughout the genome.
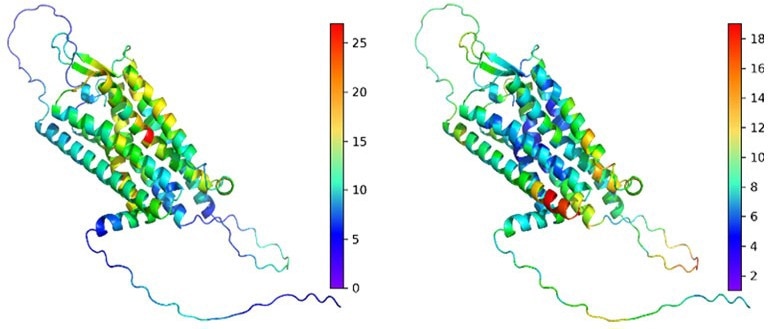 LoGoFunc identifies harmful (left) and harmless (right) genetic variations in the Vasopressin V2 receptor protein using a structure predicted by AlphaFold2. This helps explain how genetic changes affect proteins. Image Credit: Stein et al., Genome Medicine
LoGoFunc identifies harmful (left) and harmless (right) genetic variations in the Vasopressin V2 receptor protein using a structure predicted by AlphaFold2. This helps explain how genetic changes affect proteins. Image Credit: Stein et al., Genome Medicine
Unlike existing methodologies that predominantly concentrate on loss of function, LoGoFunc differentiates between various types of detrimental mutations, providing potentially valuable insights into diverse disease outcomes. The study outcomes were detailed in the online edition of Genome Medicine on November 30th, 2023.
Genetic variations have the capacity to modify protein function, where certain mutations enhance activity or introduce new functions (gain of function), while others reduce or eliminate function (loss of function). These alterations carry significant implications for human health and the management of diseases.
Tools presently available fall short in differentiating between gain and loss of function, which motivated us to develop LoGoFunc. This matters because these variants impact protein activity differently, influencing disease outcomes. We created an innovative tool that addresses a critical gap in the field, providing a practical way to understand the functional consequences of genetic variations on a larger scale.”
Yuval Itan PhD, Study Co-Senior Corresponding Author and Associate Professor, Genetics and Genomic Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Yuval Itan is also a Core Member of The Charles Bronfman Institute for Personalized Medicine.
LoGoFunc employs machine learning algorithms trained on a comprehensive database containing documented gain-of-function and loss-of-function mutations identified in existing literature. It takes into account an extensive array of 474 biological features, incorporating data from protein structures predicted by AlphaFold2 and network features that reflect human protein interactions.

Image Credit: Billion Photos/Shutterstock.com
When subjected to testing using datasets from the Human Gene Mutation Database and ClinVar, LoGoFunc showcased remarkable accuracy in forecasting gain-of-function, loss-of-function, and neutral variants, as reported by the researchers.
Beyond personalized medicine, LoGoFunc has implications for drug discovery, genetic counseling, and accelerating genetic research. Its accessibility promotes collaboration and offers a comprehensive view of variant impact across the human genome.”
Avner Schlessinger, Study Co-Senior Corresponding Author and Professor, Pharmacological Sciences, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Schlessinger, Associate Director at the Center for Therapeutics Discovery, added, “Therefore, we believe that LoGoFunc holds promise for precision medicine, enabling the possibility of more tailored treatments based on an individual's genetic makeup.”
The researchers emphasize that although these discoveries represent a substantial advancement, the translation of these insights into clinical applications necessitates additional validation and integration with other medical data. It is crucial to note that LoGoFunc's predictions rely on training data and inherent assumptions, underscoring the importance of ongoing validation efforts for ensuring dependable outcomes.
Given the expanding landscape of genetic data, enhancing LoGoFunc’s capabilities and broadening its scope emerge as key priorities for future research endeavors.
By bridging the gaps, the tool enhances our understanding of genetic variations that contribute to diseases, paving the way for personalized treatment strategies and drug discovery.”
David Stein, Study First Author and PhD Candidate, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Stein added, “We believe that LoGoFunc will be a powerful tool for deciphering the functional consequences of genetic variations. While its potential applications are vast, ongoing validation efforts will ensure its real-world impact.”
Source:
Journal reference:
Stein, D., et al. (2023) Genome-wide prediction of pathogenic gain- and loss-of-function variants from ensemble learning of a diverse feature set. Genome Medicine. doi.org/10.1186/s13073-023-01261-9