People may go to great lengths to fight aging, but this process is a part of life.
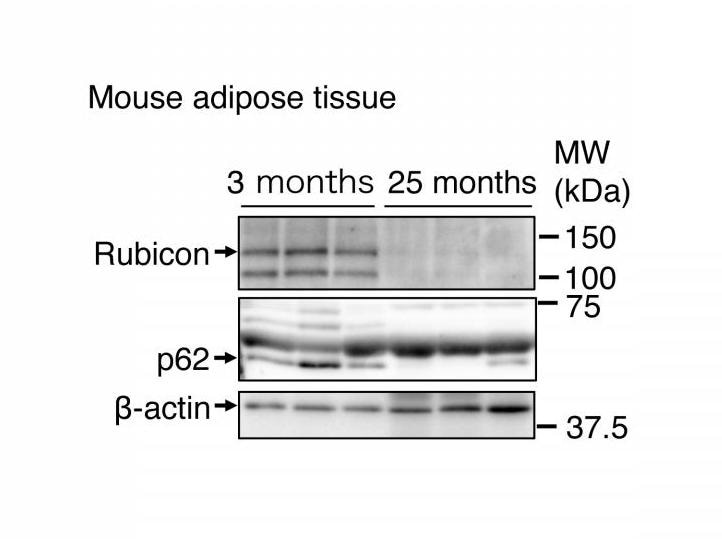
(Mouse adipose tissue) The abundance of Rubicon in adipose tissue from 25-month-old mice was significantly decreased compared with that of 3-month-old mice. Levels of an autophagic substrate, p62, also decreased with age, suggesting that autophagy increases with age. β-actin was used as the protein control. Image Credit: Osaka University.
Diabetes, high cholesterol, and fatty liver—the host of metabolic conditions known as lifestyle diseases—become more common as people become older.
But fascinatingly, several age-related metabolic disorders are induced by changes that occur within adipocytes—the fat cells that store excessive amounts of energy.
Headed by Osaka University, a team of researchers has explicitly revealed how these changes promote the onset of lifestyle diseases, with the aim of reversing the process.
The study was published in the Nature Communications journal.
Adipocytes produce hormones and cytokines that regulate the function of other metabolic organs. Age-related changes in adipose tissue result in metabolic disorders that are closely associated with life-threatening cardiovascular diseases. However, no one really knows what causes adipocyte dysfunction in aged organisms.”
Tadashi Yamamuro, Study Lead Author, Department of Genetics, Osaka University
The researchers decided to target autophagy, the process utilized by cells to remove dysfunctional or unnecessary cellular components. Prior studies had demonstrated that autophagy has a crucial role to play in the prevention of numerous age-related diseases and is perhaps involved in the process of aging.
However, most relevant was the discovery that autophagy is crucial for the longevity and regular function of normal organs, like kidney or liver.
We previously showed that a protein called Rubicon, which inhibits autophagy, is unregulated in aging tissues. We therefore hypothesized that Rubicon likely accumulates in aged adipocytes, decreasing autophagic activity and contributing to the onset of metabolic disorders.”
Tadashi Yamamuro, Study Lead Author, Department of Genetics, Osaka University
To their surprise, the researchers observed that the adipose tissue in aged mice actually contained reduced levels of the Rubicon protein, leading to increased autophagic activity.
To find out more about the fundamental mechanism, the team created a mouse line, wherein the Rubicon protein was particularly inactivated in the adipose tissue.
In the absence of Rubicon, we observed excessive autophagy in adipocytes and a decline in adipocyte function. As a result, the mice developed lifestyle diseases such as diabetes and fatty liver and had significantly higher cholesterol levels, despite being fed the same diet as control animals.”
Tamotsu Yoshimori, Study Senior Author, Department of Genetics, Osaka University
The team then went on to detect the particular proteins that were impacted by high autophagic levels, demonstrating that adipocyte function is restored by supplementing these specific proteins in the Rubicon deletion mice.
“This is a really exciting discovery with important therapeutic implications. Because age-dependent loss of adipose Rubicon causes lifestyle diseases via excess autophagy, inhibiting autophagy in adipocytes may help prevent the onset of these prevalent and potentially life-threatening conditions,” Yoshimori concluded.
Source:
Journal reference:
Yamamuro, T., et al. (2020) Age-dependent loss of adipose Rubicon promotes metabolic disorders via excess autophagy. Nature Communications. doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17985-w.