The capacity for rapid generation and validation of novel clones for protein expression and later characterization is fundamental to both industrial and academic research. Over the last 20 years, progresses in molecular biology have allowed high-throughput cloning pipelines to be developed.
However, to avoid increasing costs, this increase in throughput demands a concomitant reduction in reagent and sample input at multiple steps.
This article discusses the advantages of employing SPT Labtech’s mosquito® LV liquid handler for the miniaturization of Gateway® cloning reactions, bacterial colony PCR reactions (first to verify cloning success), and NGS library preparation (to sequence and validate cloning).
Miniaturizing these reaction volumes decreases the cost of reagents and the amount of DNA required.
Miniaturization of Gateway Cloning
The Gateway® recombination cloning technology provided by Invitrogen (by Life Technologies Ltd, UK) has transformed molecular cloning. It allows the simple and quick DNA transfer between expression vectors in high throughput.
It makes use of the bacteriophage site-specific recombination system, which enables the integration of lambda into the E.coli chromosome and the swap between the lysogenic (catalyzed by BP clonase™ enzyme mix) and lytic (catalyzed by LR clonase™ enzyme mix) pathways.
This system provides the rapid and highly efficient transfer of DNA into many vector systems. Once a gene has been cloned into an entry vector with BP clonase™, the DNA fragment can be transferred into one or more destination vectors with LR clonase™ (Figure 1).
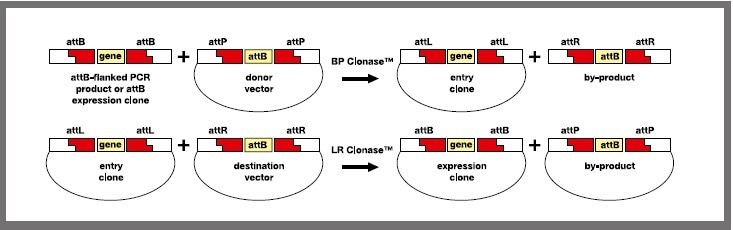
Figure 1. The Gateway cloning process involves cloning an attB-PCR product into a donor vector (attP-substrate) to form an attL-entry clone (BP recombination reaction). The entry clone is then recombined with a selected attR-destination vector to produce an attB-expression clone of choice (LR recombination reaction). (Image is modified from invitrogen, ThermoFisher Scientific, USA https://tools.thermofisher.com/content/sfs/manuals/gatewayman.pdf). Image Credit: SPT Labtech
This method has a 99% cloning efficiency and shorter cloning times, from multiple days to just one day, without ligation or restriction enzymes to maintain orientation.
This article validates the miniaturization of reaction volumes for Gateway® cloning, PCR, and NGS library preparation. Decreasing these volumes leads to a decrease in the cost and amount of DNA required.
Methods
LR and BP clonase reactions were tested at decreasing volumes with the mosquito HTS, with the volumes used in these reactions detailed in Table 1. For each reaction, the least total reaction volume was 1 µL, which contained added proteinase K to halt the reaction.
Incubation of these Gateway reactions took place at 25 °C for two hours. Subsequently, these transformed into 50 µL competent E.coli (10 µL of the advised 22 µL reaction, or the entire 1 µL and 6 µL reactions), and the whole transformation reaction was plated on a suitable antibiotic-containing media.
The subsequent resistant colonies were exposed to bacterial colony PCR (30 cycles) in reactions of declining volumes (as shown in Table 2).
Miniprep DNA was extracted from cultures of these colonies and underwent full-length plasmid NGS sequencing with NGS Nextera library preparation kits (Illumina, USA) in reactions one-tenth of the advised volume (as shown in Table 3).
The utilization of mosquito liquid handlers for miniaturizing NGS library preparation is detailed in SPT Labtech’s application notes on the company’s website.
Results
Antibiotic-resistant colonies were acquired for all transformations irrespective of volumes utilized for the BP and LR clonase reactions.
Despite a decrease in the reaction volume being accompanied by a decrease in the number of resulting colonies, even the 1 μL reactions produced greater than 100 colonies (as shown in Figure 2).
A series of resultant colonies were screened using bacterial colony PCR for each reaction. This was to ensure that an insert of the correct length was obtained. All colonies that were screened in this way signaled that the LR and BP clonase reactions were successful (as displayed in Figure 3).
Final expression constructs were fully validated using NGS sequencing from miniaturized Nextera NGS library preparation reactions. The miniaturized reaction volumes accomplished a full coverage of plasmid sequences.
Table 1. Miniaturizing BP and LR reaction volumes compared to the recommended volumes (μL). Source: SPT Labtech
| BP or LR reaction |
22 μL
(recommended vol) |
6 μL |
1 μL |
| pDONR or pDEST vector 50 ng/μL |
[2] |
[1] |
[0.2] |
| att-PCR product or entry clone 50 ng/μL |
2 |
1 |
0.2 |
| BP/LR clonase II |
[4] |
[1] |
[0.15] |
| TE buffer |
[12] |
[2] |
[0.15] (0.15) |
| Proteinase K |
(2) |
(1) |
(0.15) |
Table 2. Miniaturizing colony PCR reaction volumes compared to the recommended volumes (μL). Source: SPT Labtech
| Colony PCR reaction |
22 μL
(recommended vol) |
5 μL |
1 μL |
| Single bacterial colony suspended in water |
2 |
1 |
0.2 |
| 10x Taq reaction buffer with dNTPs |
[2.5] |
[0.5] |
[0.1] |
| 10 μM forward and reverse primers |
[0.5] |
[0.1] |
[0.02] |
| Taq polymerase (25 U/mL) |
[0.125] |
[0.025] |
[0.005] |
| Water |
[20] |
[3.4] |
[0.675] |
Table 3. Miniaturizing Nextera NGS library preparation reaction volumes compared to the recommended volumes (μL). Source: SPT Labtech
| Nextera reaction |
50 μL
(recommended vol) |
5 μL |
| Plasmid DNA (5 ng/μL) |
10 |
2.4 |
| TD buffer |
[25] |
[2.5] |
| TDE1 |
[5] |
[0.1] |
| Water |
[10] |
[0] |

Figure 2. Colony counts from one series of BP clonase reactions comparing the transformation volumes of 1 μL and 5 μL to the recommended 10 μL (LR clonase reactions provided similar results). Image Credit: SPT Labtech
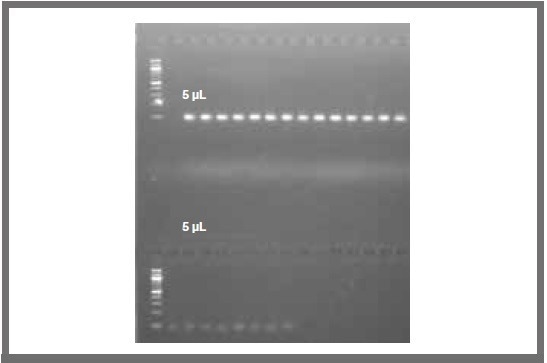
Figure 3. Comparison of 1 μL and 5 μL total reaction volumes for PCR based bacterial colony screening following the BP clonase reaction (LR reactions provided similar results). Image Credit: SPT Labtech
Conclusions
Miniaturization is a straightforward yet effective method for increasing the throughput while decreasing sample input and costs in molecular biology workflows. This study revealed substantial reductions in costs and reaction volumes for bacterial colony PCR reactions, Gateway cloning reactions, and Nextera NGS library generation reactions.
Total reaction volumes decreased from the usual volume of 25 µL to only 1 µL with the mosquito LV liquid handler, demonstrating an excellent opportunity to make significant savings in cost.
The true positive-displacement liquid handlers manufactured by SPT Labtech provide the following:
- Rapid, accurate, and reliable low-volume pipetting (from 25 nL to 5 μL)
- Reduction in DNA/RNA input
- Reduction in cost
- Low dead volume
- Ease of use
- A low-cost instrument with a compact footprint
- Ease of integration into automated workflows
Relative to the manufacturer’s suggested volume of 22 µL, this represents a 22-fold decrease for each of the BP and LR clonase reactions and a minimum 10-fold decrease relative to the low-volume adaption of the Gateway cloning protocol at this site.”
Dr. John Reece-Hoyes, Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research (NIBR), Cambridge, USA
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by SPT Labtech. The original author wishes to thank Dr. John Reece-Hoyes and Aye Chen, Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research (NIBR), Cambridge, MA, USA for providing the data presented in this article.
About SPT Labtech
We Design and Manufacture Robust, Reliable and Easy-to-Use Solutions for Life Science
We enable life scientists through collaboration, deep application knowledge, and leading engineering to accelerate research and make a difference together. We offer a portfolio of products within sample management, liquid handling, and multiplexed detection that minimize assay volumes, reduce material handling costs and put the discovery tools back in the hands of the scientist.
At the Heart of What We Do
Many of our innovations have been born out of the desire to create solutions to existing customer problems; and it’s this ethos that drives SPT Labtech’s R&D efforts. Our strengths come from the trust our customers have with us to develop truly unique, automated technologies to meet their needs. We combine cutting edge science with first-rate engineering to put customers at the heart of everything we do.
A Problem-Solving State of Mind
The substantial breadth of expertise within our company enables us to be involved in the full life cycle of our products from the initial design concept, mechanical and software engineering and prototyping, to final manufacture and sale. These qualities allow us to offer the best possible technical and mechanical support to all the equipment that we supply, hence maintaining excellent client relationships.
Sponsored Content Policy: AZoLifeScience.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.