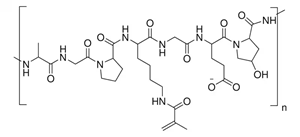
Gelatin methacryloyl, often called gelatin methacrylate or GelMA, is a gelatin biomaterial functionalized with methacrylate. The gelatin amine groups are chemically changed with methacrylate groups, which, when coupled with light and a photoinitiator, can be photopolymerized to produce a hydrogel with a three-dimensional network that closely resembles the original extracellular matrix (ECM).
GelMA is commonly utilized as a scaffold for cell culture and tissue regeneration because it provides a favorable environment for cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation. The degree of methylation and crosslinking density can be varied to change mechanical strength, degradation rate, and gelation behavior.
Many of the GelMAs now available exhibit significant variance and inconsistency. To address this, the TissueFab(R) Discrete GelMAs were created to produce a particular level of methacrylation with little batch-to-batch variability.
Application
- Tissue engineering - including bone tissue, cartilage tissue, epidermal tissue, and cardiac tissue
- Regenerative medicine- includes injectable tissue constructions and endothelial cell morphogenesis
- Drug and cell delivery - in the form of microspheres and hydrogels
- Surface coatings- of medical devices and implants to increase biocompatibility and release therapeutic cargoes
Features and Benefits
- Specific degree of methacrylation- A small methacrylation peak provides for better reproducibility, lower batch-to-batch variability, and increased uniformity of gel characteristics and cell activity
- Biocompatibility- GelMA comprises RGD sequences, which are present in collagen and other natural ECM proteins and stimulate cell adhesion, proliferation, differentiation, and maturation of distinct cell types
- Biodegradability- GelMA includes MMP-degradable sites that cells may detect and destroy enzymatically. This enables the encapsulated cells to breakdown and restructure the GelMA matrix before repopulating with their own cells and tissues, which is a significant objective in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine
- Tunability- TissueFab(R) Discrete GelMAs are available in a variety of substitution levels, which affect hydrogel stiffness and mechanical characteristics and can be utilized to recapitulate and accommodate various native tissues
- Bioprintability- TissueFab(R) Discrete GelMAs are widely employed in the area of 3D bioprinting owing to their unique gelation capabilities and the ability to manufacture complicated cell-encapsulated 3D structures with good cell viability using extrusion or other techniques
TissueFab® Discrete GelMA
Linear Formula: (C32H48N9O11)n
Source: Merck
| |
Product No. |
Description |
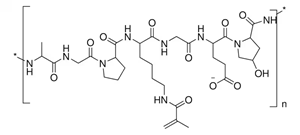 |
938416 |
170-195 boom, 50 % degree of substitution |
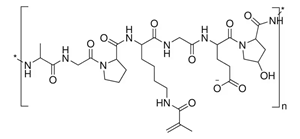 |
938408 |
300 bloom, 80 % degree of substitution |
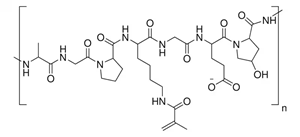 |
938904 |
300 bloom, 50 % degree of substitution |
TissueFab® Discrete GelMA
Linear Formula: (C34H54N9O11)n
Source: Merck
| |
Product No. |
Description |
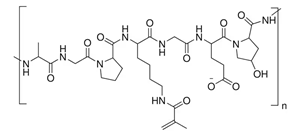 |
938890 |
gel strength 300 bloom, 20 % degree of substitution |
 |
938424 |
90-110 bloom, 50 % degree of substitution |