Overview
The EpiCorneal 3D human tissue model offers an extremely predictive non-animal option to assess corneal infection, wound healing, and tissue regeneration. It may also be used to represent diseases including dry eye and corneal infection.
Technology
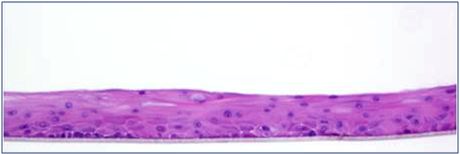
Image Credit: MatTek
The normal human corneal epithelial cells used in MatTek’s EpiCorneal tissue model have been cultivated to produce a stratified, squamous epithelium that closely resembles the natural human corneal tissue. The corneal cells differentiate to create a multilayered structure while being cultivated on specially designed cell culture inserts with serum-free media.
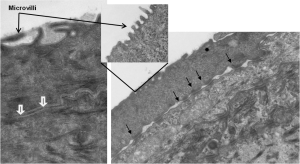
TEM Analysis of EpiCorneal illustrates the presence of 1) microvilli, 2) tight junctions (white arrows), and 3) desmosomes (black arrows). Image Credit: MatTek
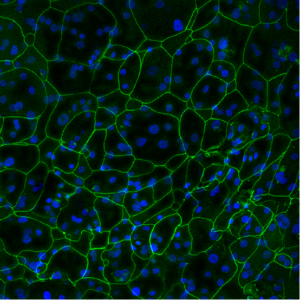
Tight Junction Protein ZO-1 (green). Image Credit: MatTek
EpiCorneal, a tissue with mitotic and metabolic activity used in drug delivery and drug research, has barrier qualities that are similar to those of the human cornea. Numerous cytokines recognized to be crucial in inflammation and diseases such as dry eye can be stimulated in EpiCorneal. Furthermore, the sophisticated 3D tissue model expresses drug transporters and metabolizing enzymes particular to the cornea.
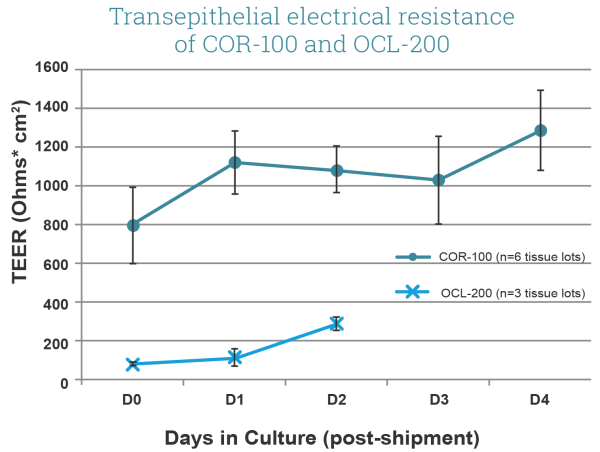
Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER) of EpiCorneal (COR-100, comprised of corneal epithelial cells) and EpiOcular (OCL-200, comprised of keratinocytes) tissue models. Note high TEER of COR-100 (avg. >600 Ω*cm2) when compared to OCL-200 (~200 Ω*cm2). Culture area is 0.6 cm2. Image Credit: MatTek
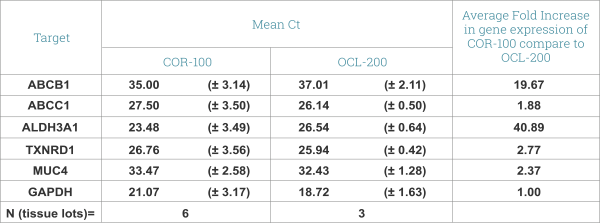
Expression of drug transporters and cornea-specific markers in EpiCorneal. qPRC data shows expression of ABCB1(p-gp) and ABCC1 (CFTR/MRP) – ATP-binding cassette, efflux transporters, multidrug resistance proteins with important role in drug disposition and distribution. Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 3 (ALDH3-A1) promotes resistance to UV and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-induced oxidative damage in the cornea. Pyridine nucleotide oxidoreductase (TXNRD1 or TrxR1) protects against oxidative stress. MUC4 – Mucin 4 is found predominantly in the most superficial cell layers in stratified corneal epithelium. Image Credit: MatTek
Human relevance
EpiCorneal produces corneal-specific markers and has a structural morphology that is similar to that of the human cornea in vivo.
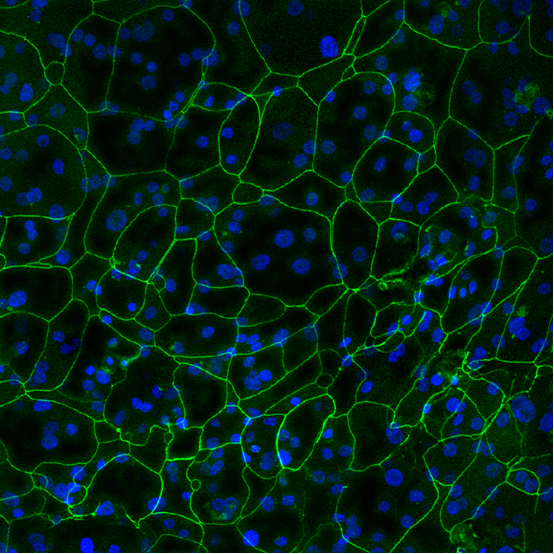
Image Credit: MatTek
Applications
- Corneal drug delivery and corneal toxicity: EpiCorneal accurately mimics the physiology, 3D tissue architecture, and function of the human cornea for use in pharmaceutical research applications.
- Model compound drug delivery
- Latanoprost drug delivery
- Corneal wound healing
- Dry eye disease